Building the User Interface
To implement the Contact Us form, we'll create a homepage with two input fields: email and body, where users can enter their contact information.
Requirements
- Followed all steps of the Quick Setup Guide for building
- HTML knowledge
Create a directory for pages
First, create a directory for your pages within the app directory:
mkdir -p app/views/pages
-p: an option to be able to create multiple nested directories at once.
Tip
You can have multiple files with the same path, so organizing your files clearly is essential.
Create a home page file
We will use HTML and Liquid templating to create the form structure and input fields. Create an index.html.liquid file in app/views/pages/ and add the following HTML code:
app/views/pages/index.html.liquid
<h2>Contact Us</h2>
<form>
<div>
<label for="email">Email</label>
<input type="text" name="contact[email]" id="email">
</div>
<div>
<textarea name="contact[body]"></textarea>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Send">
</form>
You might notice that we used index.html.liquid for our homepage file instead of index.html. This is because our tool can download websites and store them in HTML format, which can still be rendered by platformOS. Although using .liquid is not strictly necessary, we recommend it for consistency and ease of use.
Tip
The file extension .html.liquid specifies HTML as a format and Liquid as a render engine, allowing the use of both HTML and Liquid templating. This makes it easy to render dynamic content using platformOS. Read more about formats.
Using Path to the File as Default Route
The recommended approach for defining routes is to use the file path as the default route. This method uses the name of the file as the path, which enhances user experience and maintainability.
For example, the slug of the file app/views/pages/index.html.liquid will automatically default to /, making it clear and easy to find that this file represents the homepage.
Advantages of Using the File Path
- Clarity: The file name directly indicates the content it represents.
- Maintainability: Future modifications are easier since the path clearly relates to the file.
Exceptions and Advanced Usage
In some cases, such as creating RESTful URLs, you may need to use slugs. For example, to follow RESTful conventions for a /contacts/create page, you would use a slug contacts.
For more detailed information on using RESTful URLs, refer to this guide.
By default, use the file path for clarity and simplicity, but know that slugs are available for more complex routing needs.
Tip
The homepage slug is /, which will work for
Deploy and check
Save your file. Since you have already enabled the code syncing feature (pos-cli gui serve staging --sync or pos-cli sync staging), any changes saved to the file will automatically sync with the instance.
Now, visit your homepage URL (https://your-instance.staging.oregon.platform-os.com/) to see the Contact Us form:
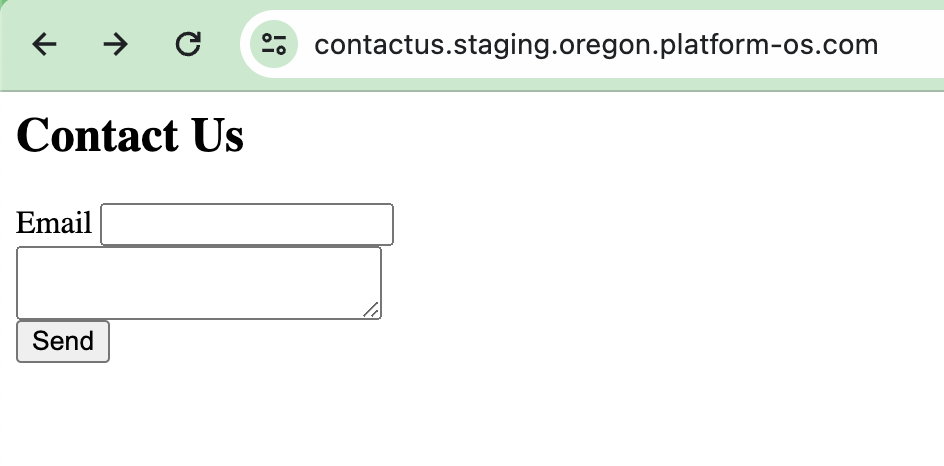
With these steps completed, your Contact Us form should be set up and ready for further development, including validation and handling form submissions. Let's proceed to implementing the backend logic and validations in the next sections!
If the sync feature is not enabled, you can manually deploy your file with the following command:
pos-cli deploy staging