Your platformOS Toolkit
To understand how platformOS works, it's helpful to first get familiar with its core components and toolchain.
Development IDE
As a developer, you’ll work on your applications locally using your preferred IDE, such as Visual Studio Code with the platformOS extension, and manage your source code with a version control system like Git.
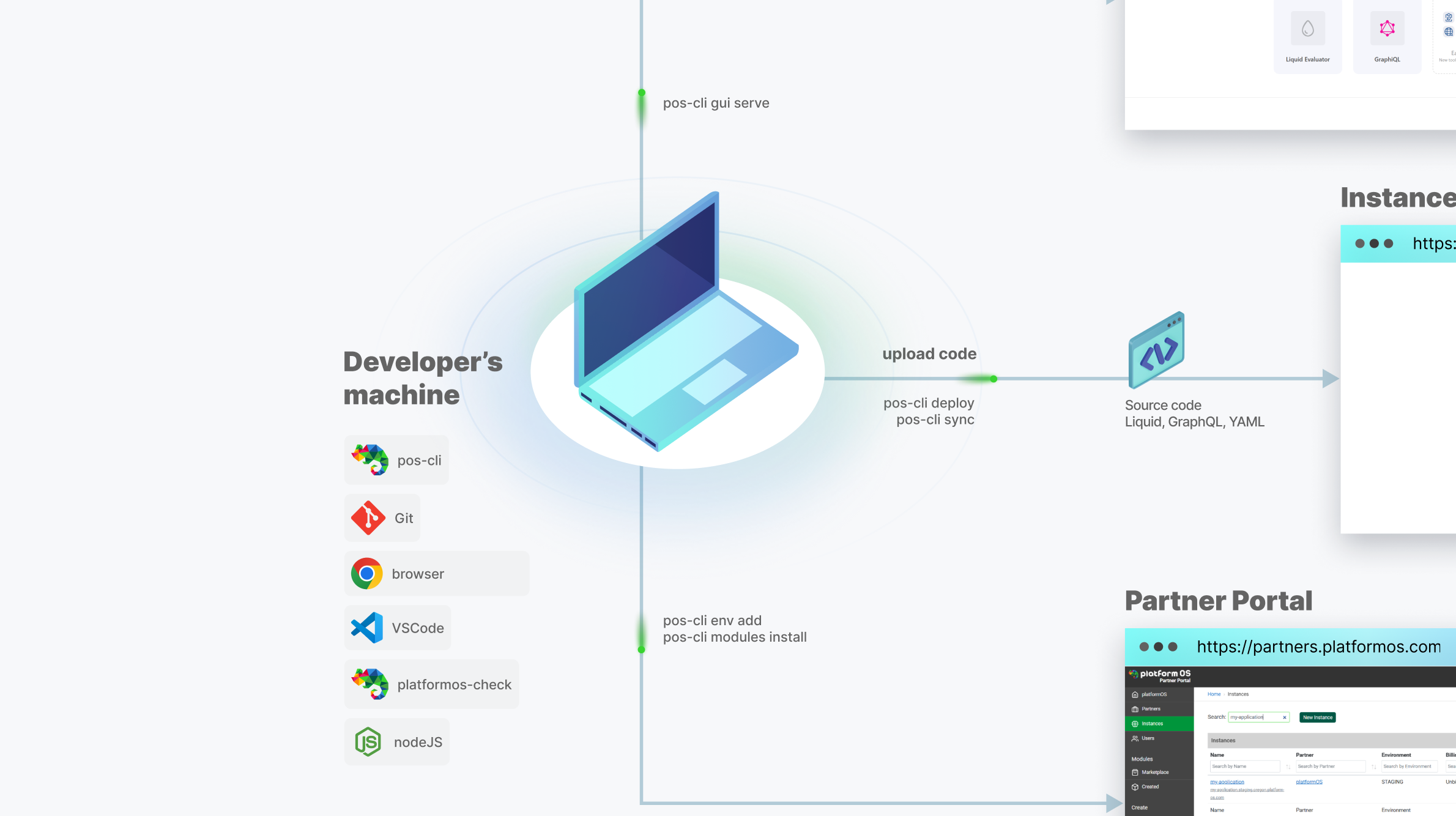
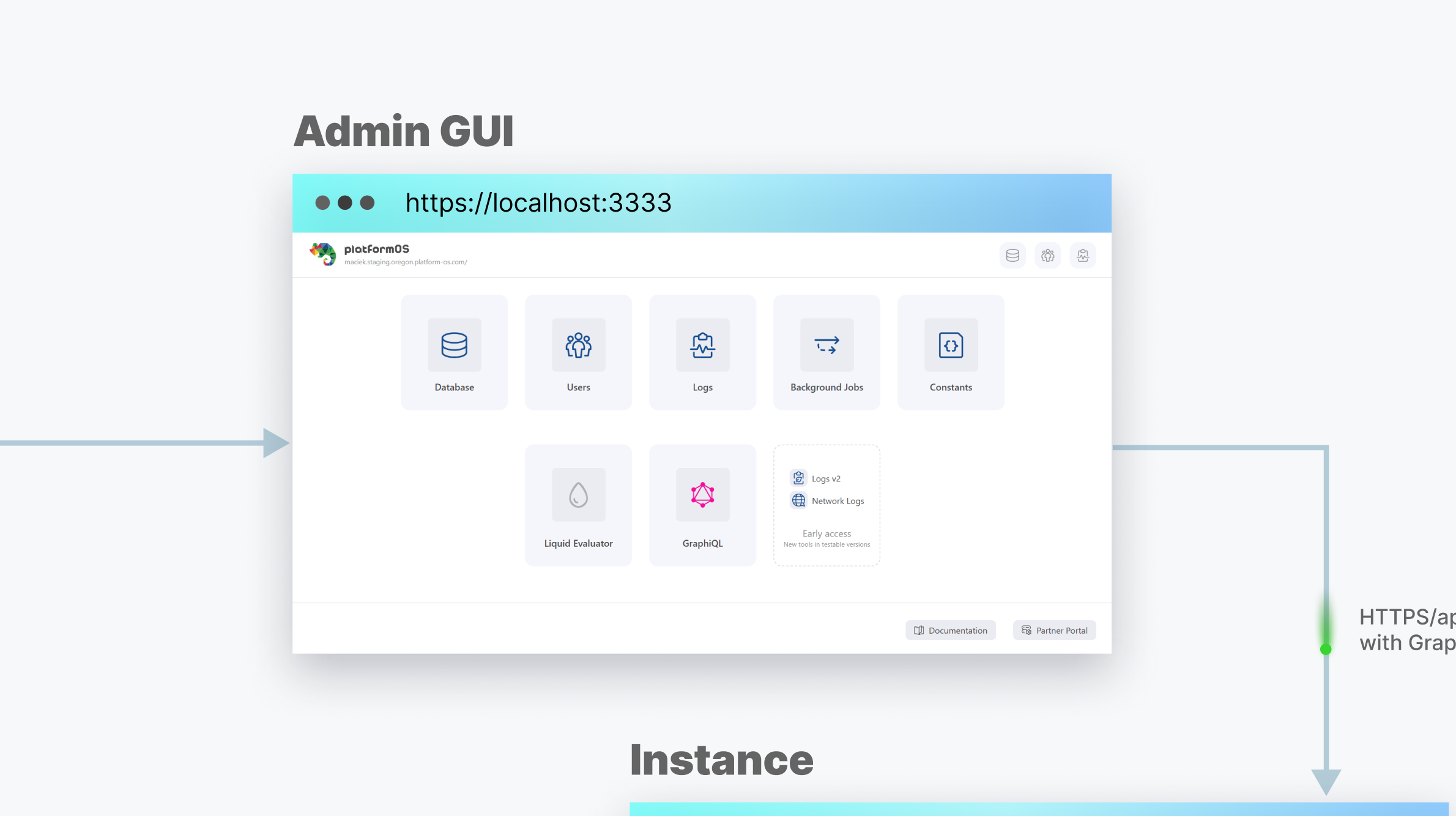
A key part of the workflow is the pos-cli client, which syncs files from the local environment to the connected development Instance. It also allows you to launch a local Admin GUI with access to application logs, a database management UI, background jobs UI, a GraphQL Explorer, and more.
Instances and Partner Portal
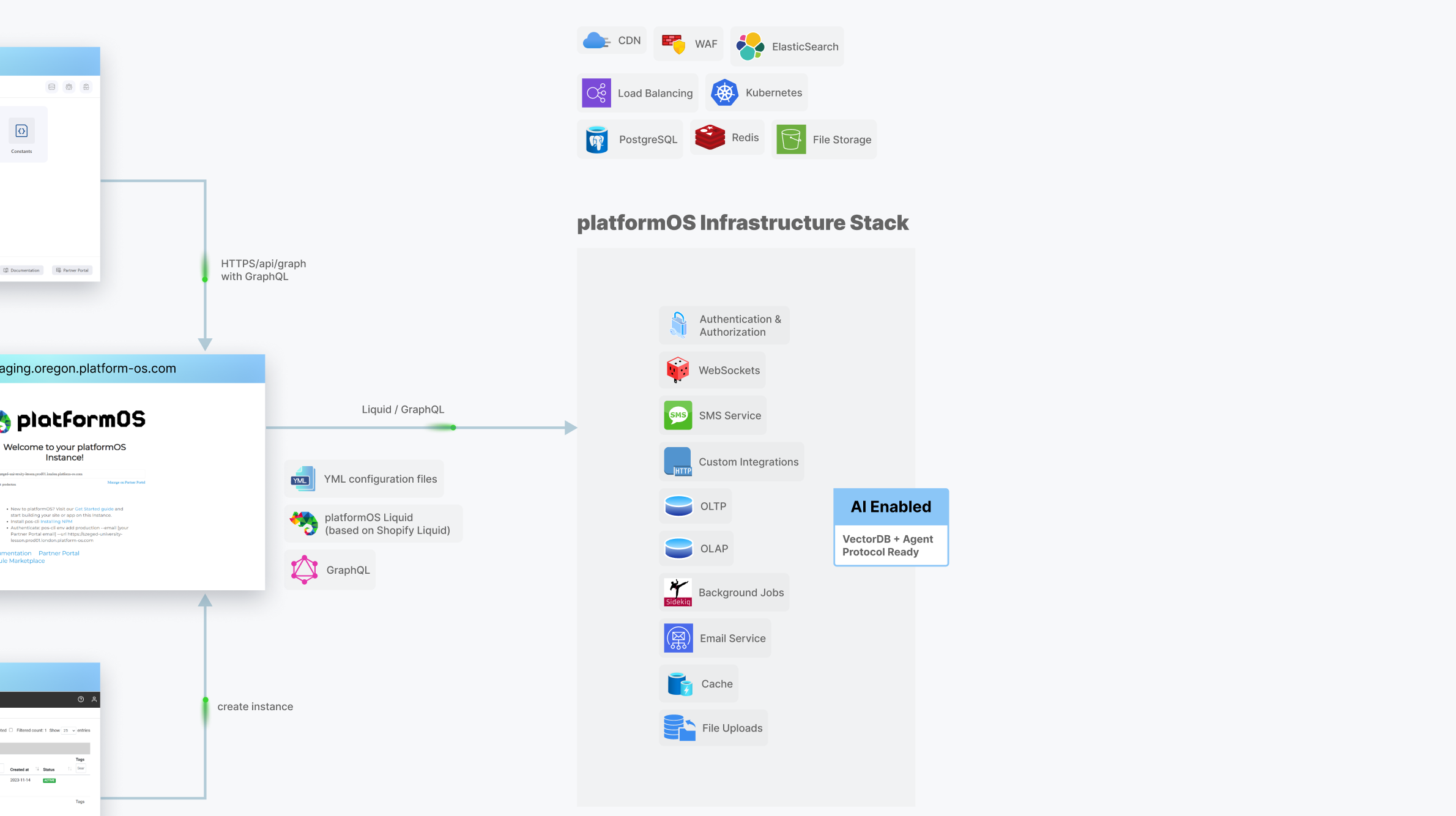
The code you write will be automatically uploaded to your Instance (a runtime environment accessible via HTTP) whenever you save the file, thanks to the pos-cli client running in the background. To get started, you’ll first create an instance through the Partner Portal with just a few clicks.
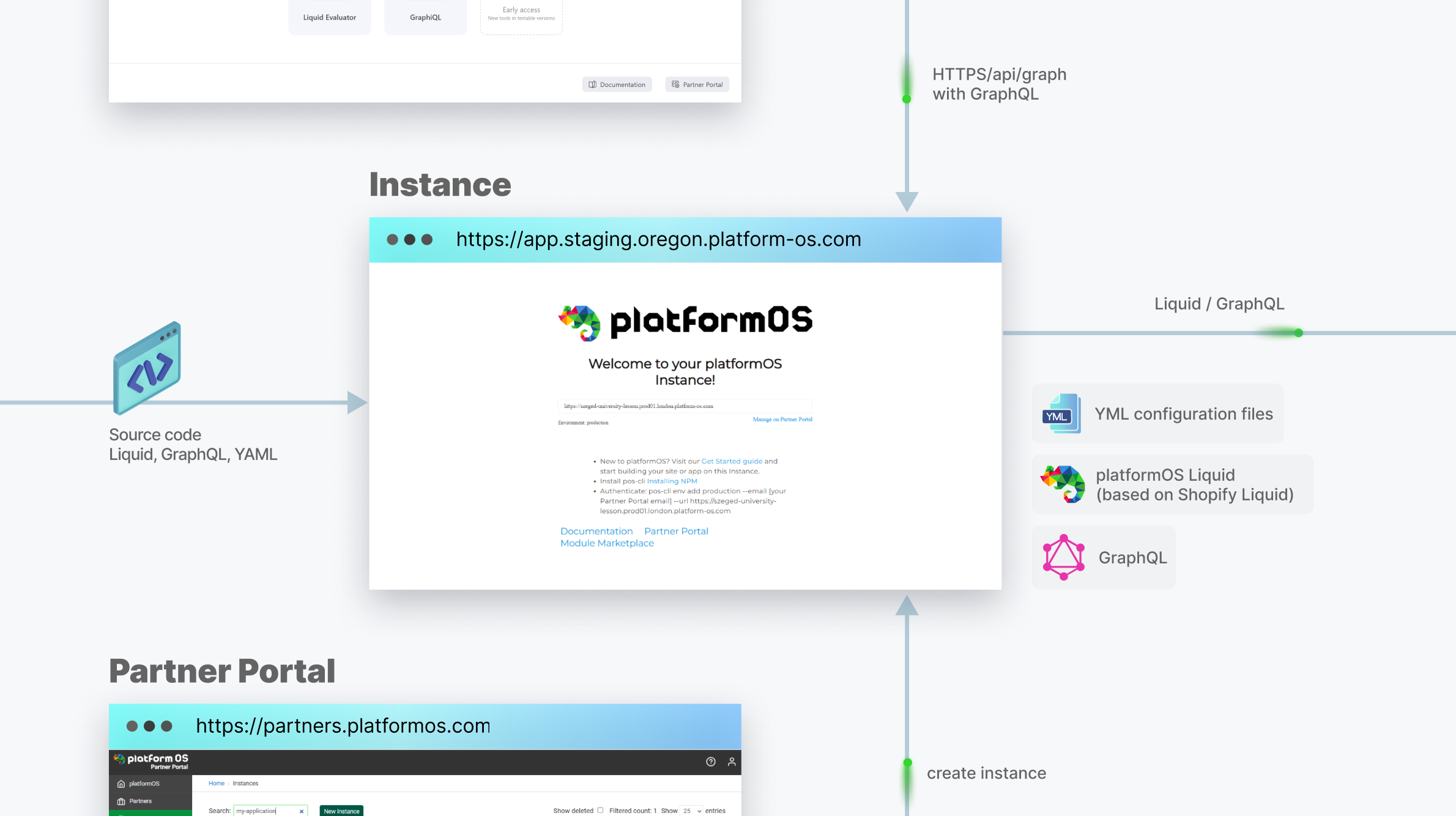
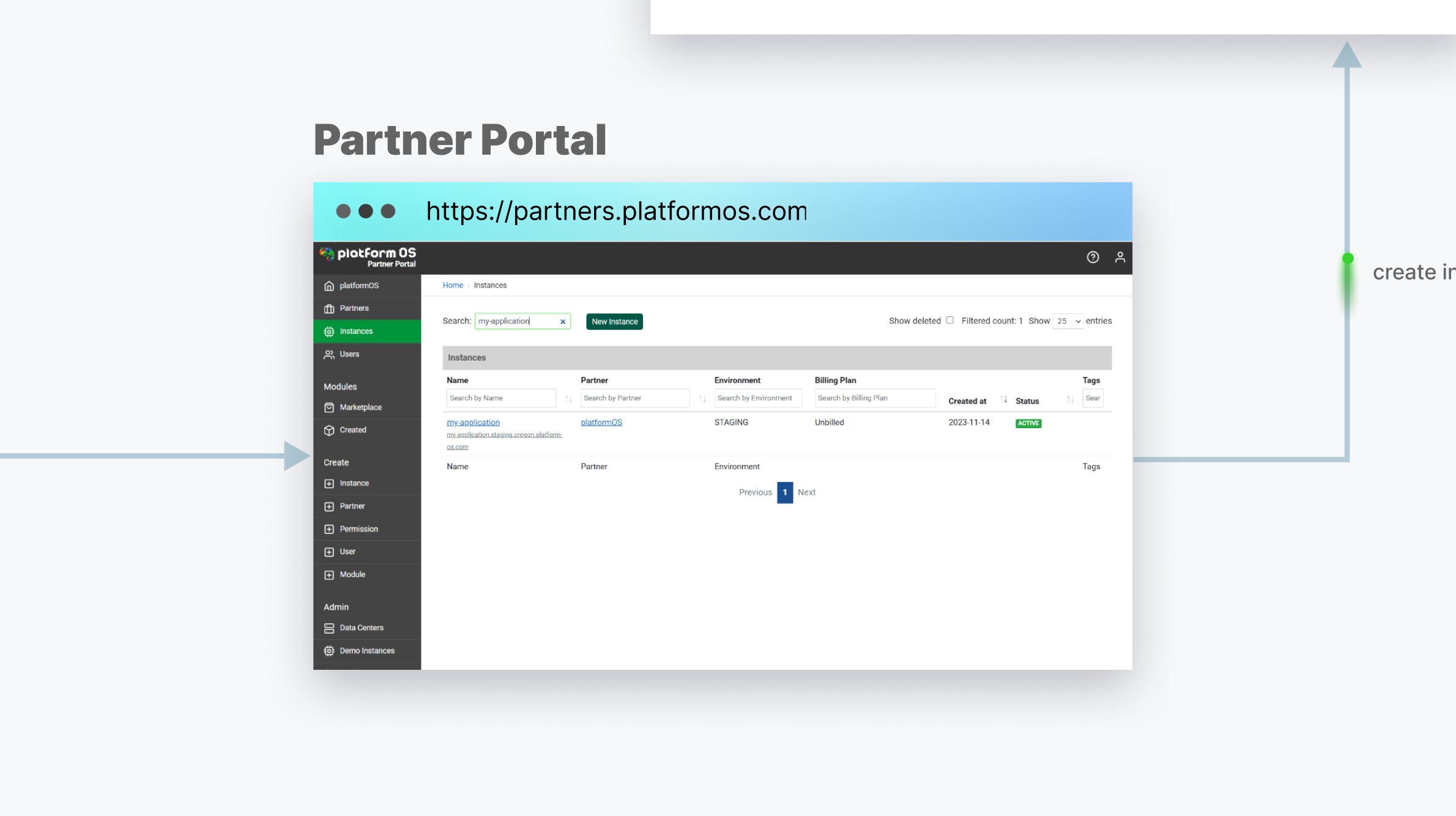
The Partner Portal serves as the central hub for creating and managing Instances, controlling user permissions, and handling infrastructure configurations such as DNS settings and automated SSL certificate generation for production environments.
Abstraction layer and Infrastructure
Your app is built using Liquid (based on Shopify Liquid), GraphQL, and YAML: a set of abstraction layers that give you control over business logic, data access, and configuration. You’ll use GraphQL queries and mutations to interact with the built-in, managed infrastructure—including PostgreSQL, Redis, ElasticSearch, and support for Vector Databases to enable AI embeddings and semantic search. YAML configuration files let you define your database schema, routing, and other settings in a clear, maintainable format.
Thanks to these layers, each Instance functions as a secure, sandboxed environment, fully isolated from others. platformOS also supports WebSockets for real-time features and is AI Agent Protocol–ready, making it a future-proof foundation for building AI-enhanced applications.
Open-Source Modules and Resources
Building a complex application from scratch is a challenging task and a significant investment. That’s why we’ve created a set of open-sourced modules that provide essential functionality, such as user authentication, RBAC authorization, OAuth integrations, 2FA, and payment processing, as well as general architectural patterns that help developers write maintainable code and implement unit tests.
We’ve also open-sourced repositories to make it easy to set up CI/CD pipelines via GitHub Actions. These pipelines can run E2E tests (for example, using Playwright), execute unit tests provided by the pos-module-tests module, and invoke the platformos-check linter to catch syntax errors, dead code, undefined variables, and style guide violations - helping teams maintain code quality.
List of platformOS Tools
In short, to support your workflow, platformOS provides a suite of tools:
- the Partner Portal for Instance management
- the platformos-check linter,
- pos-cli command line tool to deploy source code from your local computer and to provide various useful tools for developers, like for example an admin GUI for interacting with instance data, logs, background job and more
- our open-sourced modules and repositories
- VSCode platformOS Liquid extension and follow our documented best practices on this documentation site.