Using Message Length and Email Validators
The next step is to ensure that the email provided by the user looks valid and that the message body is between 10 and 200 characters long.
Core Module Validators
The core module provides essential helpers for data validation, so we don’t need to write the validators from scratch. These validators handle various checks such as:
- Ensuring all required fields are present
- Verifying uniqueness
- Confirming data types (e.g., numbers are indeed numbers and not letters)
You can find the validators in the core module’s modules/core/public/lib/validations directory.
Set up Length validation
First, we will set up the length validation to enforce these constraints. Let’s use the pre-implemented length validation from the core module documentation.
Copy the following length validation code into your /lib/commands/contacts/create/check.liquid file:
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'title', minimum: 3
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'title', maximum: 130
Modify for our use case
Modify the code to validate the body field instead of title with the appropriate length constraints (minimum 10, maximum 200):
app/lib/commands/contacts/create/check.liquid
{% liquid
assign c = '{ "errors": {}, "valid": true }' | parse_json
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'body', minimum: 10
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'body', maximum: 200
assign object = object | hash_merge: c
return object
%}
Add allow_blank argument
You might notice that the LSP is complaining that the allow_blank argument is missing, so let’s add that. You can explicitly say that allow_blank is false:
app/lib/commands/contacts/create/check.liquid
{% liquid
assign c = '{ "errors": {}, "valid": true }' | parse_json
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'body', minimum: 10, allow_blank: false
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'body', maximum: 200, allow_blank: false
assign object = object | hash_merge: c
return object
%}
The allow_blank argument in the validation function controls whether the field can be empty. Setting allow_blank: false means that if the body field is present, it must meet the specified length constraints (between 10 and 200 characters).
This means:
- If the user does not provide any input for the
bodyfield, the field is considered optional and the validation will not fail. - If the user provides input for the
bodyfield, the input must be between 10 and 200 characters long. If it doesn't meet these criteria, the validation will fail and appropriate error messages will be logged.
Set up email validation
Next, we will use the pre-written email validator from the core module:
function c = 'modules/core/validations/email', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'email'
Modify for our use case
Adjust the code and add it to your check.liquid file:
app/lib/commands/contacts/create/check.liquid
{% liquid
assign c = '{ "errors": {}, "valid": true }' | parse_json
function c = 'modules/core/validations/email', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'email'
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'body', minimum: 10, allow_blank: false
function c = 'modules/core/validations/length', c: c, object: object, field_name: 'body', maximum: 200, allow_blank: false
assign object = object | hash_merge: c
return object
%}
The newly added line uses the email validator from the core module to ensure the provided email address is in a valid format.
Using c: c variable
We always provide c: c to the validation functions to keep storing all the errors. This approach ensures that if multiple fields are invalid (e.g., both email and body), all errors are collected and can be displayed simultaneously. By storing them inside the c variable, we maintain a comprehensive list of validation errors.
Test email validation
Now that we've set up the validators for email and message length, it's time to test how they work. We will test with both invalid and valid data to see how our validation logic handles them.
Test using invalid data
Navigate to your contact form and fill in with invalid data. Use an invalid email format and/or type a message that is shorter than 10 characters, then submit it.
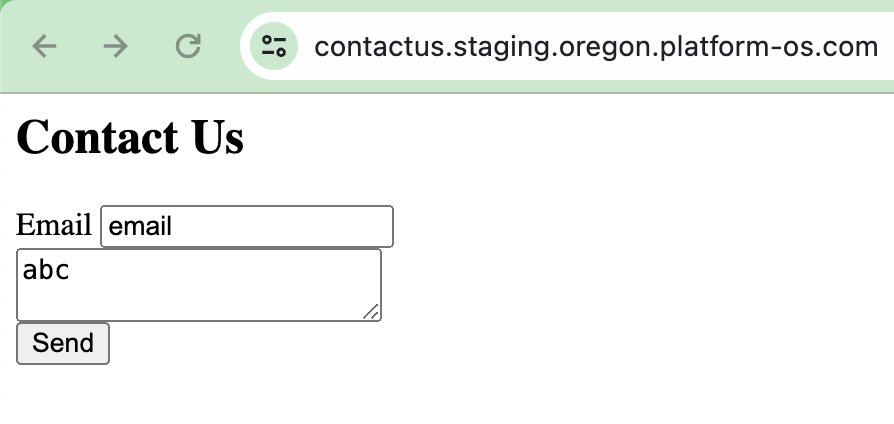
Go to http://localhost:3333/logs and check the logs to verify that the validation errors are logged correctly.
You should see entries indicating validation errors. For example:
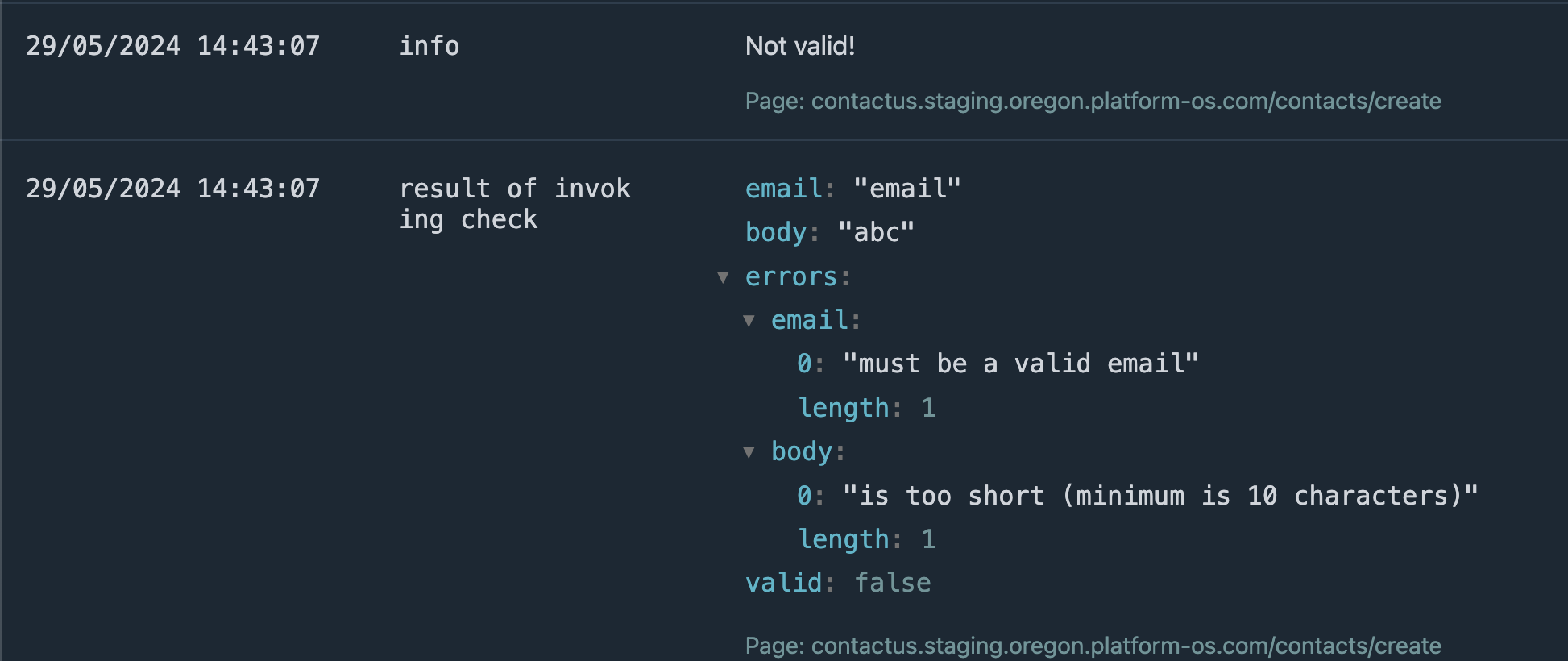
[2024-05-31 05:01:48.817Z] - info: Not valid!
path: /contacts/create page: contacts/create partial: commands/contacts/create
[2024-05-31 05:01:48.817Z] - result of invoking check: {"email":"email","body":"message","errors":{"email":["must be a valid email"],"body":["is too short (minimum is 10 characters)"]},"valid":false}
Test using valid data
Now, navigate back to your form, enter a correctly formatted email address and provide a message that is between 10-200 characters, then submit it.
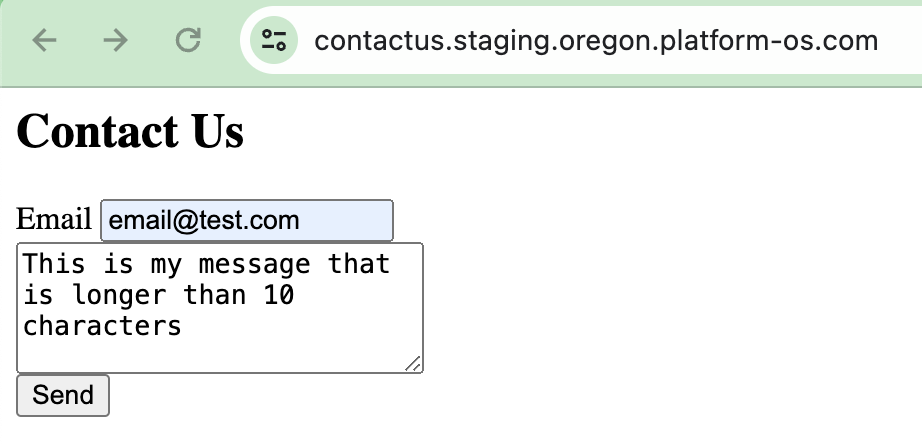
Go to http://localhost:3333/logs and check the logs to verify that the validation passed without errors. You should see entries indicating that the validation succeeded. For example:
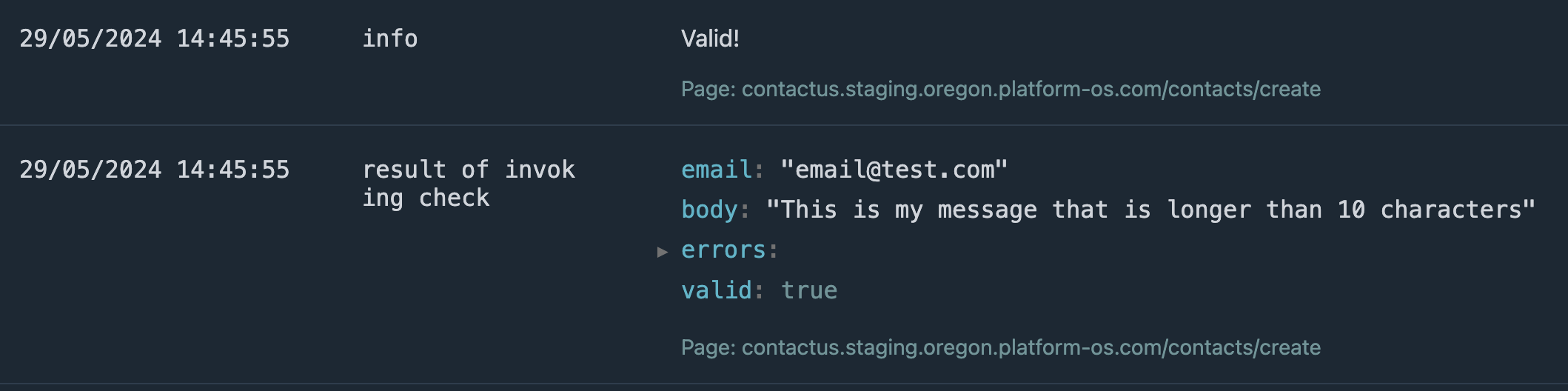
[2024-05-31 05:03:28.627Z] - info: Valid!
path: /contacts/create page: contacts/create partial: commands/contacts/create
[2024-05-31 05:03:28.628Z] - result of invoking check: {"email":"[email protected]","body":"message long long","errors":{},"valid":true}
path: /contacts/create page: contacts/create partial: commands/contacts/create