Setting Up an Endpoint and Understanding Files Structure
In the previous step, we created the schema definition file contact.yml and the GraphQL mutation file create.graphql, and we confirmed that data can be successfully saved using the mutation. At this stage, your app\ directory structure should look like this:
app
├── graphql
│ └── contacts
│ └── ✅ create.graphql
├── schema
│ └── ✅ contact.yml
└── views
└── pages
└── index.html.liquid
Now we’re going to set up an endpoint that to handle form submissions and utilize the GraphQL mutation.
We first need to create the /contacts/create endpoint. This involves setting up the /contacts/create page.
Create the contacts directory
In the app/views/pages directory, create a new directory named contacts:
mkdir app/views/pages/contacts
Create the create.liquid file
Navigate into the contacts directory and create a file named create.liquid. Add the following content to the file:
app/views/pages/contacts/create.liquid
---
method: post
---
Hello {{ context.params }}
{% graphql result = "contacts/create",
variables = {
email: context.params.contact.email,
body: context.params.contact.body
}
%}
This file sets up a POST endpoint and displays the parameters submitted through the form.
It also triggers the create.graphql mutation, with an explicit mapping of values from {{ context.params }} to the required GraphQL variables.
We will improve this implementation in the upcoming steps, but for the sake of consistency, we want to have a fully working version that utilizes all the components we've created so far.
We are going also to explain what {{ context.params }} is doing soon, in the Understanding context.params chapter.
Test the endpoint
To test if the endpoint is working correctly, go to the homepage of your Contact Us form. Enter test data into the fields and click on the Send button.
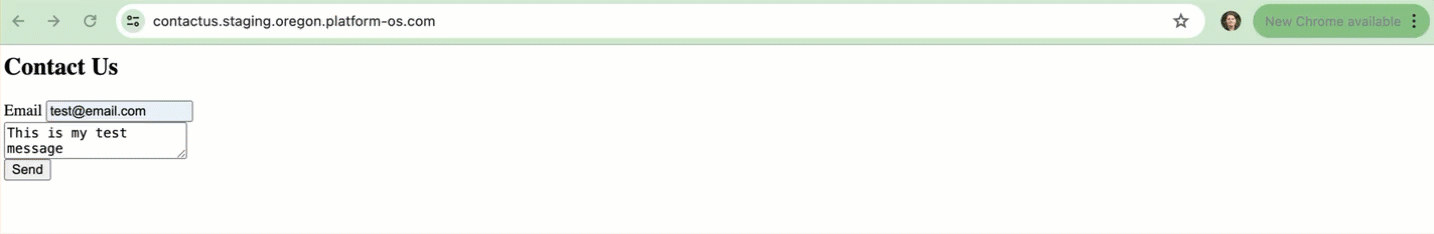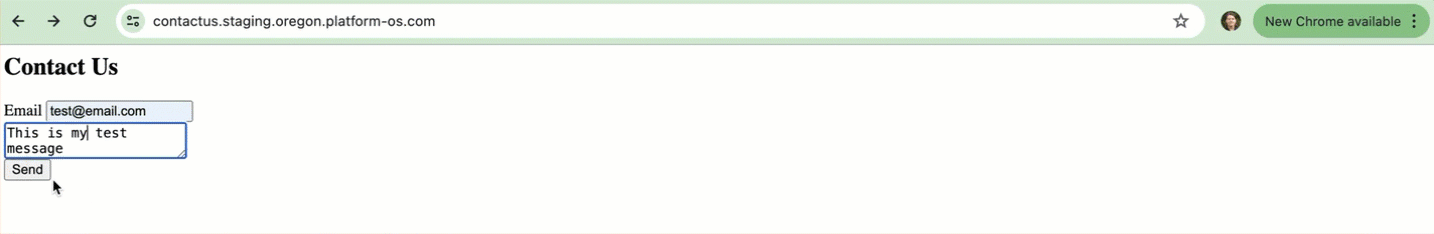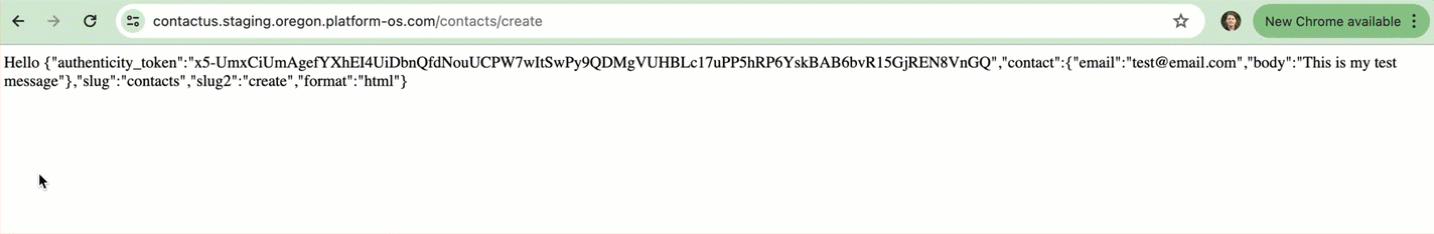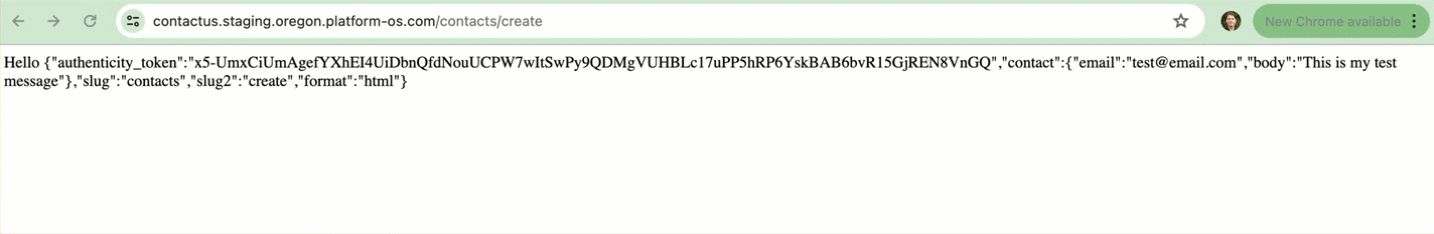
You should see a response similar to the following:
Hello {"authenticity_token":"rPROtKzFREOlK2WE89sNi0SOySB65jawjwWdxiEsKrDWK-kP6SbXDkgpK2COHCYjBpxVJ7lLADn-6hJCnbuNVQ","contact":{"email":"[email protected]","body":"This is my test message"},"slug":"contacts","slug2":"create","format":"html"}
In the response, you will see authenticity_token and contact objects, which include the email and body provided in the form.
This response comes from {{ context.params }} in our create.liquid.
Understanding file structure
Let's stop here to explain how in PlatformOS, file names and their structure aren't random — they follow a convention-based approach to connect features automatically without extra configuration.
Here's a breakdown of why the file names must correspond:
Convention Over Configuration
Instead of writing lots of configuration files to connect parts of your app, PlatformOS assumes standard locations and names work together automatically.
PlatformOS knows that a POST request to the URL /contacts/create should be handled by the file app/views/pages/contacts/create.liquid because the file path matches the URL and the file contains method: post in its frontmatter.
Similarly, the GraphQL mutation finds the contact data structure because table: contact in create.graphql matches the filename app/schema/contact.yml.
You don't need a separate model mapping file.
Automatic Variable Mapping
PlatformOS automatically takes incoming data (like from form submissions) and makes it available as variables within your code.
When the form in index.html.liquid is submitted, the fields named contact[email] and contact[body] are sent. In create.liquid, this data automatically becomes available in the {{ context.params }} object.
This allows you to easily access context.params.contact.email and context.params.contact.body to pass them to the GraphQL mutation create.graphql which expects $email and $body variables.
Routing and Page Views
The structure of your app/views/pages/ directory directly defines the URL routes for your application.
The existence of app/views/pages/contacts/create.liquid automatically creates a route accessible at /contacts/create.
There's no need for a separate routes file; the directory structure is the routing configuration.
Directory Structure Overview
Let's take a look at our current directory structure:
app
├── graphql
│ └── contacts
│ └── 📄 create.graphql ← Defines how contact data is saved
├── schema
│ └── 📄 contact.yml ← Defines data structure (email, body)
└── views
└── pages
├── contacts
│ └── 📄 create.liquid ← Handles POST requests from the form
└── 📄 index.html.liquid ← Renders the contact form
How These Files Work Together
-
index.html.liquid– Contact Form
This file renders the initial contact form.
<form action="/contacts/create" method="post">
It defines action="/contacts/create" and method="post".
This tells the browser that when the form is submitted, it should send a POST request to the URL /contacts/create.
It also defines two input fields for the email and message (body):
<input type="text" name="contact[email]" id="email">
<textarea name="contact[body]"></textarea>
-
/contacts/create- Routing the Request
PlatformOS receives the POST request for /contacts/create.
It looks inside app/views/pages/ for a structure matching the URL path contacts/create.
It finds the directory contacts and the file create.liquid.
The URL path /contacts/create maps directly to the file path app/views/pages/contacts/create.liquid.
-
/contacts/create.liquid– Request Handler
PlatformOS checks create.liquid to see if it's configured to handle POST requests.
The frontmatter --- method: post --- explicitly tells that this file is the handler for POST requests to its corresponding URL /contacts/create.
The method: post in the frontmatter matches the method="post" from the HTML form. If the method didn't match (e.g., the form sent a GET request), this file wouldn't be executed for that request.
When a POST request is made, the form fields are automatically passed into the {{ context.params }} global object.
Then, the GraphQL mutation defined in graphql/contacts/create.graphql is explicitly triggered using variables extracted from this object.
{% graphql result = "contacts/create",
variables = {
email: context.params.contact.email,
body: context.params.contact.body
}
%}
-
contact.yml– Schema Definition
This file defines what a contact record looks like. It specifies that it has email and body properties.
The filename contact.yml defines the name of the data model or table as contact.
This contact name is used elsewhere (specifically in the GraphQL mutation) to refer to this specific data structure.
-
create.graphql– GraphQL Mutation
This file contains the logic to create a new contact record in the database.
The location graphql/contacts/create.graphql logically groups this operation under "contacts" and the action "create". While not strictly enforced by routing like the views/pages files, it's the standard convention to easily find the relevant mutation.
The mutation itself explicitly references the contact table and its data structure defined in contact.yml.
It expects variables ($email, $body) and maps them to properties (name: "email", name: "body"), which correspond to the properties defined in contact.yml.
The form field names contact[email] and contact[body] in index.html.liquid use a convention (model_name[property_name]).
When submitted, they are automatically mapped to the variables expected by the GraphQL mutation.
Summary
| Component | File Name | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Schema | contact.yml |
Defines contact table for the DB |
| Mutation | create.graphql |
Mutates records in contact table |
| Form Action Handler | create.liquid |
Handles POST request to /contacts/create |
| Form Page | index.html.liquid |
Calls correct form action |
Read more about the Directory structure.